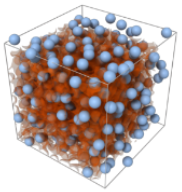
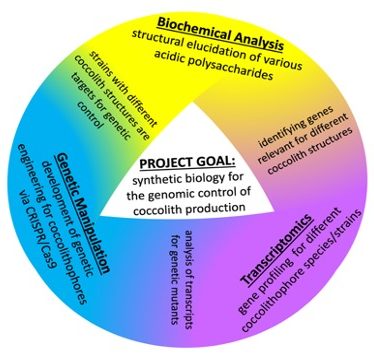
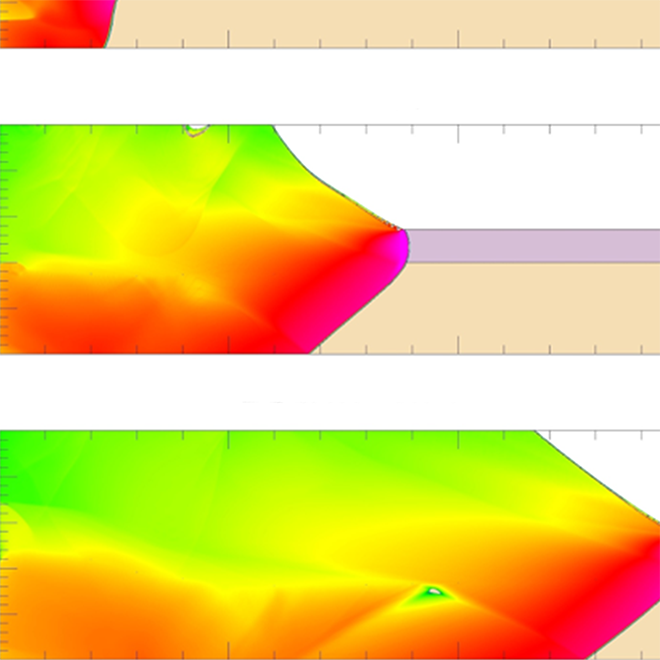
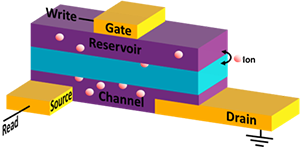
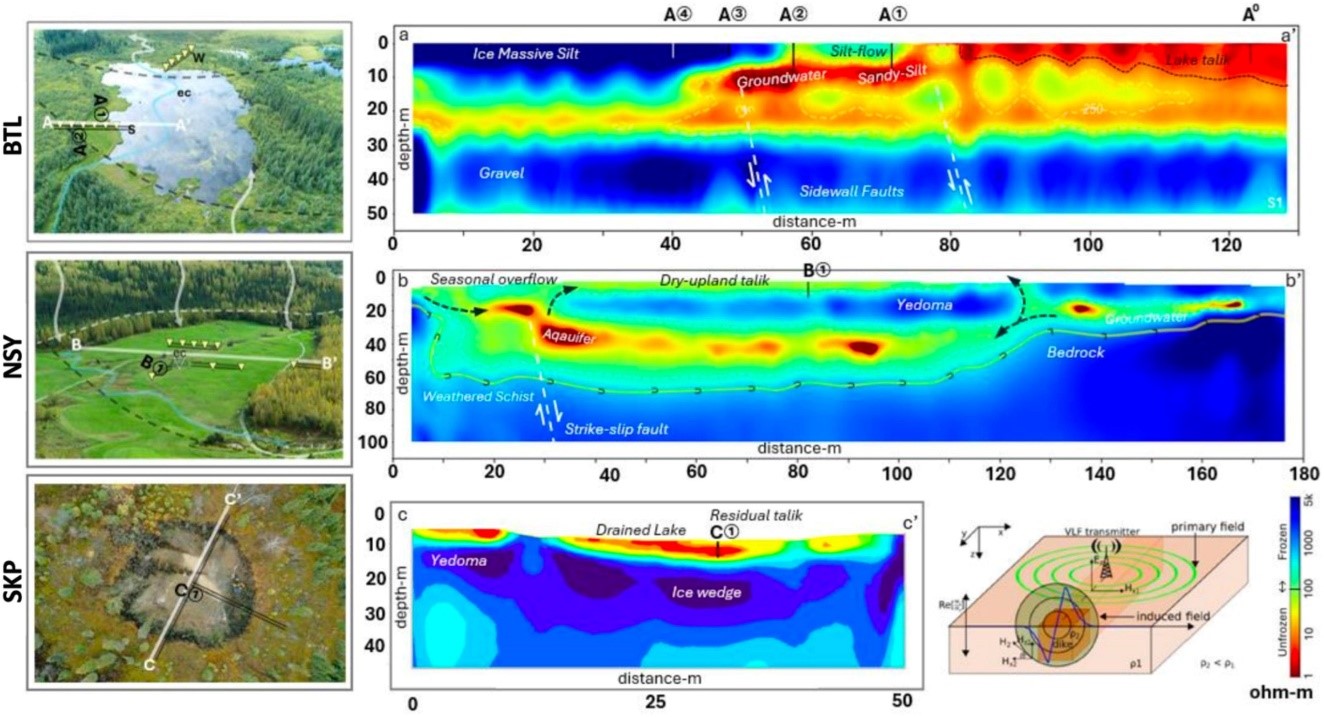
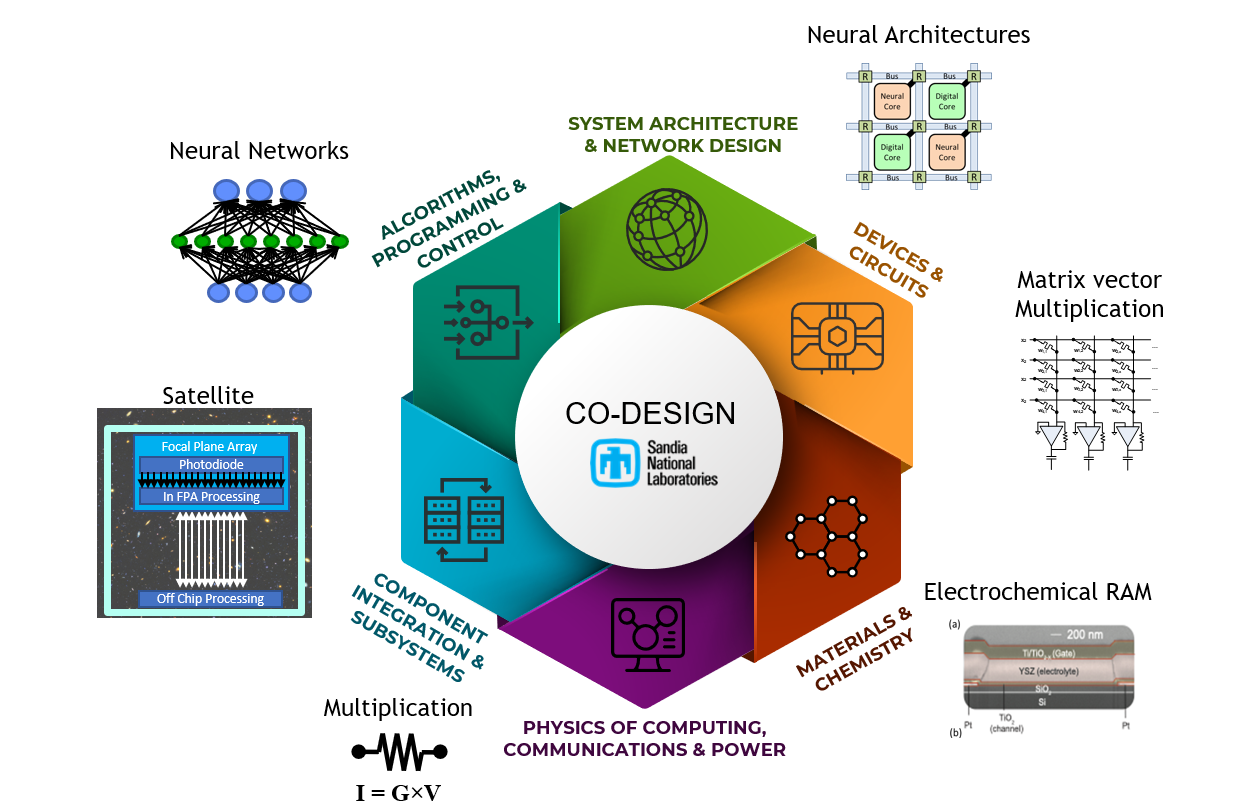
News Article, May 9, 2023 • Multiscale materials modeling fundamental insight into microscopic mechanisms that determine materials properties in nuclear stockpile applications that leverage radiation harden semiconductors, advanced manufacturing, shock compression, and energetic materials. This LDRD team including three postdoctoral researchers developed a new ML surrogate model for density functional theory using deep neural networks to...