
Copperhead program wraps up
The Copperhead program was initiated in 2008 to support the Joint Improvised Explosive Device Defeat Organization in Iraq and Afghanistan as an improvised explosive device detection sensor. The IED detections were used by the military to avoid critical injuries and deaths. Sandia has received more than $400 million in funding for the Copperhead program since its inception. With troop reductions in Afghanistan and funding shifts, the Copperhead program ceased operations on March 15, 2020. (2000, 5000)
Breakthrough in quantum photonic platform
Sandia’s National Security Photonics Center at MESA achieved multiple world’s first results in developing integrated photonic chips that manipulate single atoms for quantum computing and sensor applications. Generating precise optical signals to address atomic transitions, quantum photonics can shrink a quantum system from a car-sized table to a computer chip using heterogeneous integration. Record results included a silicon photonic (side-band modulator) chip performing atom cooling, trapping, state preparation and detection; lowest optical loss ultraviolet waveguides; ultra-narrow linewidth vertical cavity surface-emitting vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSEL) at 780 nanometers; and high-power-handling suspended waveguides. (5000)

Low Altitude and Terrestrial Transmitter System
The Sandia Advanced Radio Frequency Systems group has worked with six cross-community partners to advance the Low Altitude and Terrestrial Transmitter System, a highly reliable global communication system that ensures operational capability in hostile and contested environments. The team’s efforts have resulted in direct requirement generation and cross-agency coordination for warfighter support and eventual significant distribution of hardware worldwide. LATTS is highly expandable and provides the ability to transmit a variety of secure signals with near on-demand command and control capability. This system leverages expertise in both hardware and secure waveforms and in turn advances state-of-the-art RF electronics and sensing. Sandia’s depth and breadth of RF expertise enables the development of cutting-edge solutions for critical national security needs. (5000, 8000)
Multimission RF Architecture implemented across Radar ISR Portfolio
Sandia is implementing the LDRD-funded Multi-Mission Radio Frequency Architecture and associated Radio Frequency Module on next-generation systems for deployed programs. The MMRF architecture enables arbitrary waveform generation/detection needed in current mission spaces. The technology permits future integration of multi-mission technologies with minimal nonrecurring engineering and lower costs. (5000)

Open Threat Assessment Platform work for TSA
The Sandia Open Threat Assessment Platform team developed and demonstrated a next generation software integration platform for the DHS Transportation Security Administration that allows third-party applications to be deployed onto proprietary screening equipment such as baggage X-rays. Among other capabilities, the OTAP project enables nonproprietary threat-detection algorithm solutions, which result in greater detection efficacy. In August 2020, TSA, other regulators and airport operators across the globe issued a policy statement supporting open architecture and OTAP’s products specifically. (1000, 2000, 5000, 6000, 8000, 9000)
Industrial Control System Cybersecurity Symposium
Sandia hosted a two-day ICS Cybersecurity Symposium in February with more than 80 external attendees from across the federal government, including seven other government laboratories, DOE, the four military service branches, the combatant commands, the intelligence community, academia and industry. The goal was to share information on national security mission needs related to ICS cybersecurity, highlight existing capabilities and research roadmaps to address those needs. The symposium was well received by those in attendance and spurred new collaboration opportunities within the community. (5000, 9000)

Award-winning DARPA extreme MIRaGE software
To realize the potential of metamaterials, the Multiscale Inverse Rapid Group-theory for Engineered-metamaterials project team developed easy-to-use design tools for the architecture of metamaterials exhibiting exotic electromagnetic behaviors beyond what nature can provide. The project, previously highlighted in DARPA’s 60th anniversary showcase, was recognized as an FY20 Laser Focus World Innovators Platinum Award winner and nominated for an FY21 Federal Laboratory Consortium Tech Development Award. Metamaterials designed with MIRaGE will serve in specialized optics, advanced lasers, cloaking materials, thin/flat lenses and national security and space program applications. (1000, 5000)
Xyce release supports enhanced electrical simulation
Sandia’s Xyce circuit simulator team released Xyce version 7.2 to support DARPA’s Posh Open Source Hardware and Intelligent Design of Electronic Assets programs. The project is creating tools to usher in an era of 24-hour design cycles for defense-related hardware systems, shorten hardware upgrade times and enable proliferation of custom systems-on-chip. Xyce can simulate modern process nodes, including 12 nanometer FinFET-based technologies. The Xyce circuit simulator develops simulation-based evidence for nuclear weapon system qualification through large-scale, predictive simulations with quantified uncertainty for NW electrical systems. (1000)

Sandia-led center mitigates complex-wide cyber threat
The Sandia-led NNSA Cyber Intelligence Center of Excellence quickly analyzed and wrote detailed reports to share across the Nuclear Security Enterprise about the risks of the Ripple20 vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities impact a small library widely used by companies to allow their devices and software to connect to the internet. The COE’s analysis and dissemination of information was shared using tools that allow analysts to quickly understand the threat and collaborate with team members across the NNSA complex. (9000)
Annual All-Army Cyber Stakes
The Army held the 4th Annual All-Army Cyber Stakes, a U.S. government cyber practitioner exercise. The event drew thousands of competitors, both federal employees and civilians, from across the departments of Defense and Homeland Security as well as the Office of Global Affairs. Darek Jensen placed third overall and second among civilians in the competition, demonstrating his skills and helping to solidify Sandia’s technical credibility in this domain. (8000)
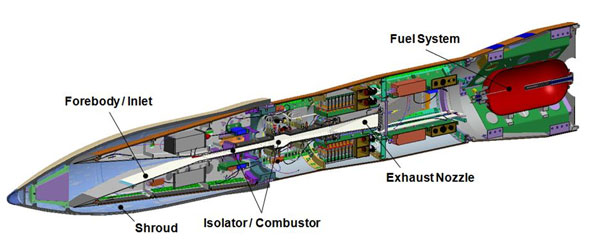
Uncertainty quantification in Scramjet combustion computations
Modeling Scramjet combustion with inclusion of uncertainty quantification involves exceptional complexity and high computational cost. Through DARPA sponsorship, Sandia demonstrated a practical approach to analyze and optimize a laboratory-scale Scramjet combustor, allowing for uncertainty in operational and model parameters. The achievement is crucial for hypersonic systems R&D, providing insights into potential paths toward applying these capabilities in supersonic and hypersonic engine designs. The work employed computational capabilities using high-fidelity Large Eddy Simulation for modeling unsteady turbulent flow, shock physics and chemical kinetic modeling of reaction processes. (1000, 8000)
Pandemic modeling analysis for COVID-19
Sandia’s cross-division COVID-19 Pandemic Modeling and Analysis team supported the DOE Office of Science in technical efforts of recovery modeling, economic modeling and analysis, data analysis and epidemiological forecasting. The work was done in coordination with Los Alamos, Oak Ridge and Argonne national labs and the National Virtual Biotechnology Laboratory, a consortium of all DOE labs. Results have been disseminated to DOE, the departments of Commerce and State, the Defense Threat Reduction Agency and the New Mexico Department of Health. (8000)
Radar to Optical Feature Extraction and Correlation flight test succeeds
The first Synthetic Aperture Radar flight to generate navigation data with ROFEC on the Sandia Facility for Advance Radar and Algorithmic Development radar system, for a live GPS-Denied operation, was successful. The ROFEC algorithm, developed under the DoD/DOE Joint Munitions Program at Sandia, is an innovative methodology that correlates images from two heterogeneous imaging modalities, SAR and optical. The flight test demonstrated that ROFEC and aircraft velocity algorithms are contenders as navigational aids in GPS-compromised environments, a huge step toward GPS-denied operational capability using Sandia systems. (5000)
National Risk Management Center
In response to an Executive Order, the Risk Analytic Methods and Support team responded to a rapid analytic request from the National Risk Management Center at the Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. Sandia used the Cyber Risk Framework it has been developing for NRMC to produce risk analytic results in eight working days, validating the Cyber Risk Framework. The results of the analysis became a large part of the DHS response to the White House request. (8000)

Successful hypersonic flight at Kauai Test Facility
Sandia employees and contractors saw their work culminate in a successful hypersonic flight test March 19, 2020, at the Kauai Test Facility in Hawaii. Sandia provided design and fabrication of the flight vehicle; preflight modeling, simulation and analysis; ground testing of common hypersonic glide body components; and launch support at the test range. The successful test and future experiments will further inform DoD’s hypersonic technology development and provide a technology maturation pathway that directly benefits future Nuclear Deterrence programs. (600, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000)