CIME is the Common Infrastructure for Modelling the Earth. It is the full-featured software engineering system for global Earth system or climate models. CIME is a set Python scripts configured with XML data files as well as Fortran soure code, and owns the model configuration, build system, test harness, test suites, portability to...
Software
Compadre Toolkit
CrossSim
CrossSim is a GPU-accelerated, Python-based crossbar simulator designed to model analog in-memory computing for any application that relies on matrix operations. This includes neural networks, signal processing, solving linear systems, and many more. It is an accuracy simulator and co-design tool that was developed to address how analog hardware effects...
Dakota
Dakota: Optimization and Uncertainty Quantification Algorithms for Design Exploration and Simulation Credibility. The Dakota toolkit provides a flexible, extensible interface between analysis codes and iterative systems analysis methods. Dakota contains algorithms for: optimization with gradient and nongradient-based methods;uncertainty quantification with sampling, reliability, stochastic expansion, and epistemic methods;parameter estimation with nonlinear...

E3SM
E3SM is an Earth System Model being developed by the DOE Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) project. E3SM Version 1 was released in 2018. E3SM Version 2 was released in 2021. The E3SM atmosphere model runs with the spectral element dynamical core from HOMME, upgraded to include new aerosol and cloud...
Genten: Software for Generalized Tensor Decompositions
Tensors, or multidimensional arrays, are a powerful mathematical means of describing multiway data. This software provides computational means for decomposing or approximating a given tensor in terms of smaller tensors of lower dimension, focusing on decomposition of large, sparse tensors. These techniques have applications in many scientific areas, including signal...
Jet Partitioner
The Jet Partitioner is a parallel graph partitioner that runs on most CPU and GPU systems (via Kokkos, a required dependency).
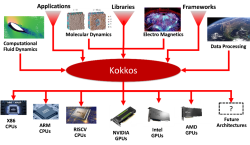
Kokkos
Modern high-performance computing (HPC) architectures have diverse and heterogeneous types of execution and memory resources. For applications and domain-specific libraries/languages to scale, port, and perform well on these architectures, their algorithms must be re-engineered for thread scalability and performance portability. The Kokkos programming system enables HPC applications and domain libraries...
Kokkos Kernels
Kokkos Kernels is a software library of linear algebra and graph algorithms used across many HPC applications to achieve best (not just good) performance on every architecture. The baseline version of this library is written using the Kokkos Core programming model for portability and good performance. The library has architecture-specific optimizations...
LAMMPS
LAMMPS, an acronym for Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator, is a classical molecular dynamics code with a focus on materials modeling. LAMMPS has potentials for solid-state materials (metals, semiconductors) and soft matter (biomolecules, polymers) and coarse-grained or mesoscopic systems. It can be used to model atoms or, more generically, as...
LAPIS
Linear Algebra Performance through Intermediate Subprograms (LAPIS) is a compiler infrastructure based on MLIR for linear algebra that targets both high productivity and performance portability.
MALA
MALA is a software package for building and deploying Scientific Machine Learning Models for electronic structure calculations, specifically density functional theory (DFT) calculations. DFT is one of the most widely used methods for simulating materials at a quantum level and predicting their properties, employed by researchers worldwide. MALA is open...
ParaView
ParaView is an open-source, multi-platform data analysis and visualization application. ParaView users can quickly build visualizations to analyze their data using qualitative and quantitative techniques. The data exploration can be done interactively in 3D or programmatically using ParaView’s batch processing capabilities. ParaView was developed to analyze extremely large datasets using...

Peridigm
Peridigm is an open-source computational peridynamics code. It is a massively-parallel simulation code for implicit and explicit multi-physics simulations centering on solid mechanics and material failure. Peridigm is a C++ code utilizing foundational software components from Sandia's Trilinos project and is fully compatible with the Cubit mesh generator and Paraview visualization...

Poblano Toolbox
Poblano is a Matlab toolbox of large-scale algorithms for unconstrained nonlinear optimization problems. The algorithms in Poblano require only first-order derivative information (e.g., gradients for scalar-valued objective functions), and therefore can scale to very large problems. The driving application for Poblano development has been tensor decompositions in data analysis applications...
Prove-It
Prove-It is a tool for proving and organizing general mathematical theorems using Python. Prove-It uses a flexible framework and a clear, concise presentation that appear like formulas one would present to colleagues on a chalkboard. Prove-It can avoid paradoxes by simply disallowing cycles in operator-operand relationships; this ensures that consistent types...
PyApprox
PyApprox provides flexible and efficient tools for credible data-informed decision making. PyApprox implements methods addressing various issues surrounding high-dimensional parameter spaces and limited evaluations of expensive simulation models with the goal of facilitating simulation-aided knowledge discovery, prediction and design. Methods are available for: low-rank tensor-decomposition; Gaussian processes; polynomial chaos expansions;...
PyNucleus
PyNucleus is a finite element code that specifically targets nonlocal operators of the form $\int_{\mathbb{R}^d} [u(x)-u(y)] \gamma(x, y) dy $ for nonlocal kernels $\gamma$ with finite or infinite horizon and of integrable or fractional type. Specific examples of such operators include the integral and regional fractional Laplacians, their truncated and...
Pyomo
Pyomo is a Python-based open-source software package that supports a diverse set of capabilities for formulating, solving, and analyzing optimization models. A core capability of Pyomo is modeling structured optimization applications. The Pyomo software package can be used to define general symbolic problems, create specific problem instances, and solve these...

pyttb: Python Tensor Toolbox
The Python Tensor Toolbox (pyttb) is a refactor of the Tensor Toolbox for MATLAB in Python. This package contains data classes and methods for manipulating dense, sparse, and structured tensors, along with algorithms for computing low-rank tensor decompositions. Tensors (also known as multidimensional arrays or N-way arrays) are used in a variety...
Qthreads
The Qthreads API is a tool that helps developers easily manage many threads in their programs. It allows them to break their programs into smaller tasks and lets the system handle the scheduling of these tasks automatically. One of its features is the ability to mark each piece of memory...

Rapid Optimization Library (ROL)
Rapid Optimization Library (ROL) is a high-performance C++ library for numerical optimization. ROL brings an extensive collection of state-of-the-art optimization algorithms to virtually any application. Its programming interface supports any computational hardware, including heterogeneous many-core systems with digital and analog accelerators. ROL has been used with great success for optimal...

Slycat
Slycat™ is a web-based system for analysis of large, high-dimensional data, developed to provide a collaborative platform for remote analysis of data ensembles. An ensemble is a collection of data sets, typically produced through a series of related simulation runs. More generally, an ensemble is a set of samples, each consisting of...
SPARTA
Stochastic PArallel Rarefied-gas Time-accurate Analyzer SPARTA is a parallel DSMC or Direct Simulation Monte Carlo code for performing simulations of low-density gases in 2d or 3d. Particles advect through a hierarchical Cartesian grid that overlays the simulation box. The grid is used to group particles by grid cell for purposes...
SPPARKS
Stochastic Parallel PARticle Kinetic Simulator SPPARKS is a parallel Monte Carlo code for on-lattice and off-lattice models that includes algorithms for kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC), rejection kinetic Monte Carlo (rKMC), and Metropolis Monte Carlo (MMC). It implements several KMC solvers whose serial computational complexity ranges from O(N) to O(NlogN) to...
Results 1–25 of 29