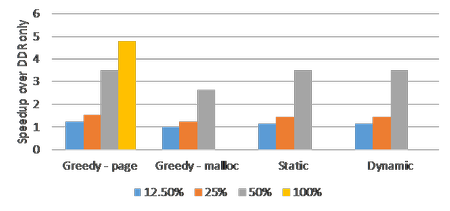
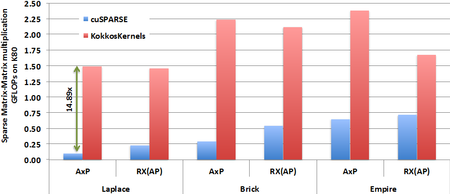
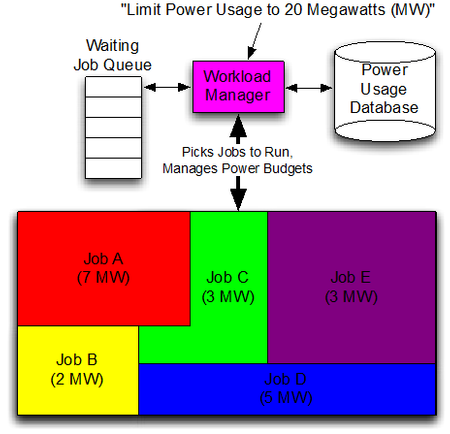
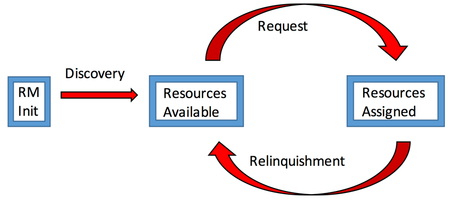
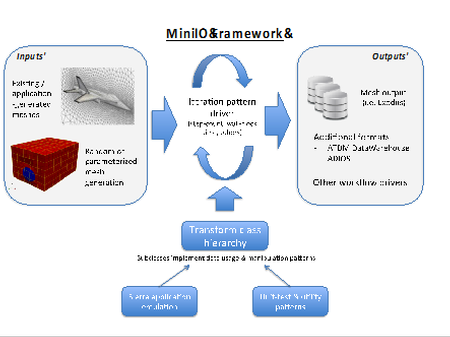
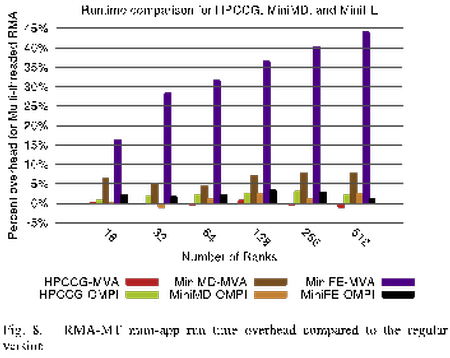
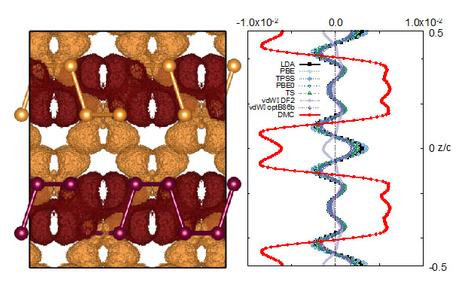
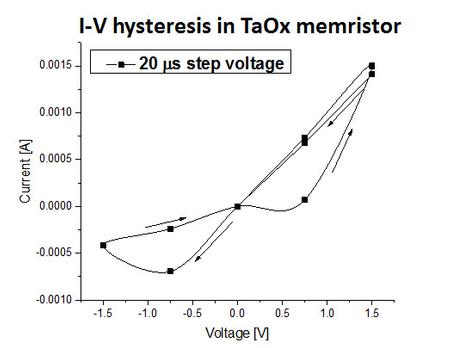
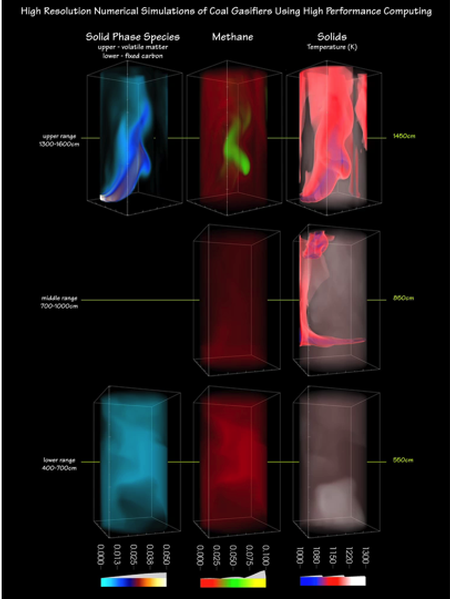
November 1, 2016 • The October 2016 issue of Computer magazine on Energy Efficient Computing contains three feature articles co-authored by Sandians, including two articles from staff in the Center for Computing Research. The article “Standardizing Power Monitoring and Control at Exascale” co-authored by Ryan Grant (1423), Michael Levenhagen (1423), Stephen Olivier (1423), Kevin...