Award, September 19, 2012 • Invited Talk, Knox College Computer Science Department.
Search
Suma George Cardwell
Staff Page • Principal Member of Technical Staff. Biography Dr. Suma George Cardwell is a Principal Member of Technical Staff in the Center for Computing Research at Sandia National Laboratories. She completed her PhD and MS in Electrical and Computer Engineering at Georgia Tech, Atlanta in 2015 and 2011 respectively. She has over...

System Software
Focus Area • System software research and development activities provide the software foundation that enables the scaling and performance of applications to unprecedented levels. Sandia has performed pioneering work in lightweight operating system and scalable runtime systems for some of the world's largest computing platforms. Core areas of competency are lightweight operating systems,...
Task mapping for non-contiguous allocations
Award, May 20, 2013 • Invited Talk, Boston University CISE.
Task Mapping Stencil Computations for Non-Contiguous Allocations
Award, April 2, 2014 • Invited Talk, Workshop on New Challenges in Scheduling Theory.
Team Employee Recognition Award
Award, April 22, 2013 • Internal - employee recognition award, Sandia National Laboratories. For demonstrated success in transforming Dakota to a production computational tool in support of Sandia's core NW mission and a growing external...
Team Employee Recognition Award, QCAD
Award, April 15, 2013 • Internal - employee recognition award, Sandia National Labs.
Technical Program Committee
Award, January 4, 2016 – September 24, 2016 • Society/professional leadership, 5th International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications, and Informatics.
Tenth Space Computing Workshop
News Article, June 1, 2017 • The Center for Computing Research (1400) in collaboration with the Predictive Sensing Systems Group (6770) conducted the 10th annual Spacecraft Computing workshop May 30-June 2, 2017. The workshop, held at Sandia and a local hotel, focused on advanced computing for spacecraft, which require technology that functions reliably in the harsh...
Teresa Portone
Staff Page • Optimization & Uncertainty Quantification. Biography Teresa joined Sandia in January 2020. Her research focuses on assessing and enhancing model prediction fidelity to inform high-consequence decisions for national security applications, especially in the presence of uncertainty. She has expertise in methods to characterize model-form uncertainty, sensitivity analysis, Bayesian methods, and multifidelity...

test
Page •
test
Page •
The Extreme-Scale Scientific Softare Development Kit (xSDK)
Project • The goal of the xSDK is to provide the foundation of this extensible scientific software ecosystem. The first xSDK release (in April 2016) demonstrated the impact of defining draft xSDK community policies to simplify the combined use and portability of independently developed software packages. The xSDK releases have continued to attract more...

The Extreme-Scale Scientific Software Stack (E4S)
Project • The Extreme-Scale Scientific Software Stack (E4S) is an open source, open architecture effort to create a US and international collaborative software stack for high performance computing. Led by the US Exascale Computing Project (ECP), E4S provides a conduit for building, testing, integrating and delivering the open source products developed under...

The Next Platform Highlights CCR Work on Memory-Centric Programming
News Article, February 1, 2018 • A recent article from The Next Platform, an online publication that offers in-depth coverage of high-end computing, recently featured an article entitled “New Memory Challenges Legacy Approaches to HPC Code.” The article discusses a paper co-authored by CCR researcher Ron Brightwell that was published last November as part of the...

Thomas E. Voth
Staff Page • Computational Multiphysics. Biography Tom is a member of the Computational Multiphysics Department which is home to the ALEGRA multiphysics application. As a member of the ALEGRA team Tom has lead developments in contact/impact mechanics for explicit dynamics and remesh methods for Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian mechanics. Tom is also technical lead...
Thomas M. Smith
Staff Page • Computational Science. Biography My research and development interests center around two major topics. The first is discretizations of PDEs for unstructured grids such as; finite element, finite volume and discontinuous Galerkin methods. The second topic is modeling and simulation fluid flows such as; incompressible, compressible, turbulent, reacting, wave propagation and...

Three staff in the Non-Conventional Computing Technologies department (1425) recently made high-profile technical communications.
News Article, September 1, 2017 • Three staff in the Non-conventional Computing Technologies department (1425) recently made high-profile technical communications: Kenneth Rudinger coauthored a paper published in Physical Review Letters on a robust method for phase estimation for qubits: “Experimental demonstration of cheap and accurate phase estimation.” His co-authors were Shelby Kimmel, Joint Center for Quantum...
![FIG. 1: (a) RPE and (b) GST experimental sequences. Each sequence starts with the state p and ends with the two-outcome measurement M. (a) An RPE sequence consists of repeating the gate in question either L orL + 1 times. (b) In GST, a gate sequence Fi is applied to simulate a state preparation potentially different from p. This is followed by [L/|gk|I] applications of a germ—a short gate sequence gk of length |gk|. Finally, a sequence Fj is applied to simulate a measurement potentially different from M.](https://www.sandia.gov/app/uploads/sites/210/2022/06/Aidun_580-1.jpg)
Tian Yu Yen
Staff Page • Scientific Machine Learning. Biography Tian Yu joined Sandia as a postdoc in 2021. His current research focuses on methods of aleotoric and epistemic uncertainty quantification for inverse problems as well as techniques for quantifiying uncertainty in machine learning algorithms. He has a background is in measure-theoretic inversion, Bayesian inference, and...
Timothy Michael Wildey
Staff Page • Scientific Machine Learning. Biography Tim joined Sandia National Labs in January, 2011 following a postdoctoral fellowship at the University of Texas at Austin. His research interests are finite element and finite volume methods, discontinuous Galerkin methods, hybridized discretizations, a posteriori error analysis and estimation, uncertainty quantification, adjoint methods, multiphysics and...

Translating new neurons from mice to humans: the computational neuroscience of scale
Award, October 10, 2012 • Invited Talk, Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute.
Trilinos
Software • The Trilinos Project is an effort to develop algorithms and enabling technologies within an object-oriented software framework for the solution of large-scale, complex multi-physics engineering and scientific problems. A unique design feature of Trilinos is its focus on packages.

Trilinos
Project • The Trilinos Project is an effort to develop algorithms and enabling technologies within an object-oriented software framework for the solution of large-scale, complex multi-physics engineering and scientific problems. A unique design feature of Trilinos is its focus on packages.

Trinity
News Article, January 1, 2016 • The next-generation Trinity supercomputing platform project has recently achieved two important milestones. Trinity is an advanced computing platform for stockpile stewardship that is being architected and procured by the Alliance for Computing at Extreme Scale (ACES), a partnership between Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories, under the NNSA Advanced Simulation...
Trinity Program Pursuing “Power-Aware Scheduling” Through Contract with Adaptive Computing
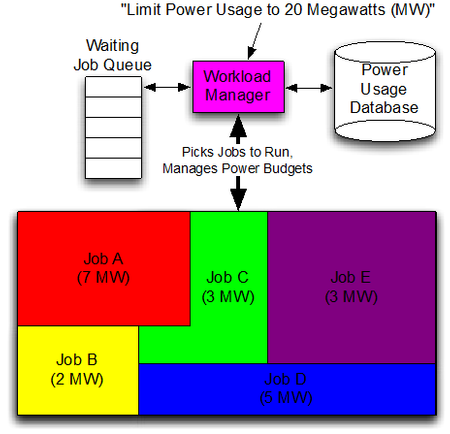
News Article, October 1, 2016 • The Trinity project has placed a new “Non-Recurring Engineering” contract with Adaptive Computing to develop “Power-Aware Scheduling” capabilities for the Trinity supercomputer, which when fully installed will consume 8-10 megawatts (MW) and have a peak computational capability of more than 40 petaflops. This work will enable power to be managed...
Results 451–475 of 499