This website is intended to serve government agencies and contractors with the use of the ASC Software through government-use agreement. Please be sure to reach out to the contact listed before starting the process.
ALEGRA
ALEGRA is a software project with an extensive set of physics modeling capabilities to simulate the response of materials that are subject to large deformations and strong shocks coupled to Maxwell equations in order to provide for magnetohydrodynamics, electromechanics and radiation transport in an arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian reference frame. ALEGRA simulations provide insight into a variety of phenomena for engineering systems including high-speed impact, penetration mechanics, explosive devices, pulsed power devices, transformers, and radiation-driven shock and damage. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Steve Bova.
Aleph
Aleph is an unstructured 3D Particle-In-Cell (PIC) low temperature kinetic plasma code developed to model plasma discharges in low pressure systems. Aleph provides self-consistent plasma evolution within electrostatic fields using the Galerkin Finite-Element-Method (FEM) with particle collisions treated using the Direct Simulation Monte Carlo (DSMC) method. Additional capabilities include coupled electrode thermal conduction to enable self-consistent thermal desorption and a suite of advanced surface and collisional models for modeling complex mixtures and plasma-surface interactions. Aleph efficiently models an extreme range of length and time scales by combining unstructured meshes with a two-decomposition treatment of the mesh. Rebalancing the particle mesh together with algorithms for dynamic particle reweighting allow problems involving hundreds of millions of elements and billions of particles to scale well up to thousands of processors on High-Performance Computers (HPCs). If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Ron Manginell.
Cascade
If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Tom Quirk.
Charon
Charon is an open-source semiconductor device modeling code, widely referred to as a TCAD (technology computer-aided design) code, developed at Sandia National Laboratories. It is written in C++ and relies on another Sandia open-source project, Trilinos, for supporting code, such as nonlinear and linear solvers, finite-element and finite-volume libraries, I/O, etc. In addition to running on most Linux-based computers Charon also supports simulation of extremely large problems on massively parallel computing systems that support the MPI standard. For more information please visit the Charon website. If you are interested in obtaining this software please Shahed Reza.
CHEETAH-MC
CHEETAH-MC is a new Monte Carlo coupled electron-photon transport code under active development that is being designed to be user-friendly and run on next-generation heterogeneous computer architectures. The software architecture of CHEETAH-MC is knowledge-enabled, component-based, and layered to provide resilience, reproducibility, and scalability. Built on the foundation of the Integrated Tiger Series (ITS), CHEETAH-MC includes multiple source and geometry representations for simulating the behavior of the electrons and photons through solids, gases, and stochastic materials. Particles can be tracked from the source through the geometry using either standard surface tracking or Woodcock tracking methods. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Joe Castro.
CTH

CTH is a multi-material, Eulerian, large deformation, strong shock wave, solid mechanics code developed at Sandia National Laboratories. It has models for multi-phase, elastic viscoplastic, porous and explosive materials. Three-dimensional rectangular meshes, two dimensional rectangular, and cylindrical meshes, and one-dimensional rectilinear, cylindrical, and spherical meshes are available. CTH has adaptive mesh refinement and uses second-order accurate numerical methods to reduce dispersion and dissipation and produce accurate, efficient results. It is written in FORTRAN 90 and C and has serial and parallel versions for UNIX and Linux workstations, Beowulf clusters, massively parallel supercomputers, macOS and Windows. Serial and parallel pre-built executables for Linux, Windows (WSL) and macOS are available. CTH provides an end-to-end simulation solution including visualization support. For more information please visit the CTH website. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Aaron Brundage.
Cubit
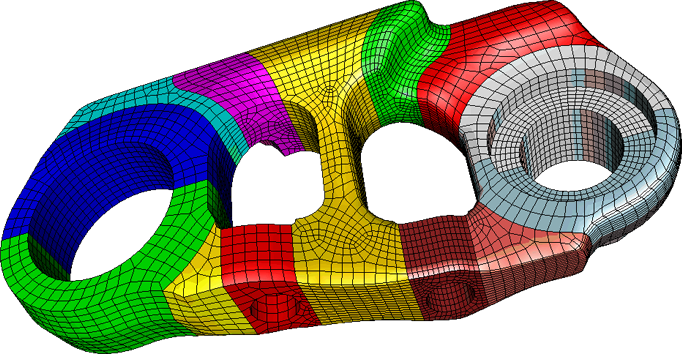
CUBIT™ is a full-featured software toolkit for geometry preparation and robust generation of two-dimensional and three-dimensional finite element meshes (grids). Its main goal is to reduce the time required to generate meshes, particularly large hex meshes of complicated, interlocking assemblies. For more information please visit the Cubit website. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Mike Skroch.
EIGER
EIGER is a massively parallel, frequency domain, boundary element method of moments Electromagnetic (EM) code. The feature set is tailored to ND problems with the ability to model very high-q cavities. Additionally, EIGER offers the ability to create wire and slot sub-cell models for coupling and use in non-ideal, dissipative materials. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact William Langston.
EMPIRE
EMPIRE is a next generation Electromagnetic (EM) Particle In Cell (PIC) plasma code which includes addition of new fluid and hybrid fluid/PIC models for simulation across a wider range of plasma regimes. EMPIRE is built on a component based architecture using Kokkos and Trilinos to achieve performance portability across next-generation computing architectures. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Richard Kramer.
Gemma
Gemma aims to provide a tool for efficiently solving frequency domain electromagnetic problems on heterogeneous computer architectures, including CPUs, GPUs,and MICs, using Sandia’s Kokkos performance portability library. Gemma includes alternative algorithms for select use cases, and relies on the
method of moments to accurately and reliably solve electromagnetic problems. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact William Langston.
ITS
ITS (Integrated Tiger Series) is a Monte Carlo photon-electron transport code for system-level modeling of a x-ray propagation into RB/RV and secondary electron production. ITS has the capability to transport directly on CAD model Combinatorial, CAD, and hybrid geometries and offers code coupling with EMPHASIS for SGEMP calculations. SCEPTRE (Sandia Computational Engine for Particle Transport for Radiation Effects) is a 1-, 2-, and 3-D deterministic transport code for Component-level modeling of x-ray propagation and secondary electron production. SCEPTRE offers multigroup cross sections generated for X-section codes and linear deterministic Boltzmann transport solvers. SCEPTRE has the capability to deploy different solvers for different particle species and discontinuous FEM (1st order) and continuous FEM (2nd order) on unstructured meshes. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Joe Castro.
LGR
LGR (Lagrangian Grid Reconnection) is a shock hydrodynamics research code using finite element methods. LGR provides explicit time stepping with mass lumping and uses Lagrange+Remesh+Remap approaches, similar to CTH and ALEGRA. With LGR, meshes remain conformal and avoid volume fractions and interface reconstruction. LGR has been optimized for GPU performance, but is also portable on all machines where the MPI and OpenMP libraries are available. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Steve Bova.
NuGET
NuGET models the external n-g radiation environment, system-level propagation of radiation into RB/RV and neutron damage in components. NuGET is able to provide an environment external to RB with prompt neutrons, prompt gamma ionizing dose, air secondary gamma production, and RB motion. NuGET similarly can provide environment internal to RB secondary gamma production. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Tom Quirk.
Plato
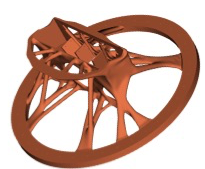
Plato allows a designer to generate designs that are optimized to meet functional requirements. The Plato environment offers an interactive design experience where the user can see the evolving design and make mid-stream corrections to guide the design optimization to better meet functional requirements. The Plato design environment runs on Windows, Linux, and Mac platforms. For more information please visit the Plato website. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Mike Skroch.
SAW
The Sandia Analysis Workbench (SAW) is a family of software applications that boost productivity and quality by making modeling and simulation easier while enforcing best practices and supporting ubiquitous V&V. Capabilities include workflow management, model building, job submission, requirements tracking, and simulation data management. The Workbench provides a user-friendly graphical interface to Sierra, CTH, DAKOTA, and other important Sandia codes. SAW strives to be a generally useful environment for computational simulation. The core SAW architecture is vendor-neutral with respect to analysis codes. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Tricia Gharagozloo.
SCEPTRE
SCEPTRE (Sandia Computational Engine for Particle Transport for Radiation Effects) is a 1-, 2-, and 3-D deterministic transport code for Component-level modeling of x-ray propagation and secondary electron production. SCEPTRE offers multigroup cross sections generated for X-section codes and linear deterministic Boltzmann transport solvers. SCEPTRE has the capability to deploy different solvers for different particle species and discontinuous FEM (1st order) and continuous FEM (2nd order) on unstructured meshes. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Joe Castro.
SeqQuest
SeqQuest is a general-purpose electronic structure code to compute energies and forces for periodic surfaces (slabs) or solids, or finite molecules. SeqQuest uses density functional theory (DFT), and is capable of calculations using either LDA or GGA, with or without spin-polarization. It will do energy minimization of atomic positions through force elimination, cell shape optimization by stress-elimination, and molecular dynamics. SeqQuest rigorously and automatically corrects for supercell effects using the Local Moment Counter Charge method. SeqQuest uses norm-conserving pseudopotentials and high-quality contracted-Gaussian basis sets in a "Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals" (LCAO) approach in its description of the electronic structure, and is a very efficient, compact code that enables very large-scale calculations (100’s, even 1000+ atoms on large memory workstations) using rather modest computational resources (single-processor work stations, or small clusters). Key to this performance is the implementation of highly efficient algorithms for the generation of the Hamiltonian matrix that scale linearly with problem size. If you are interested in obtaining this software please Dave Littlewood.
Sierra

Sierra is an engineering mechanics simulation code suite that includes coupled simulation capabilities for thermal, fluid, aerodynamics, solid mechanics, and structural dynamics. We use these simulation capabilities to predict the performance of a weapon system in normal operation as well as the response of a system in abnormal environments, such as a crash or fire. If you are interested in obtaining this software, please contact Kendall Pierson.
SPARC
SPARC (Sandia Parallel Aerodynamics and Reentry Code) simulates the aerodynamic environment and material thermal response for atmospheric flight vehicles from subsonic to hypersonic speeds, enabling the design, development, and analysis of such vehicles with higher fidelity and greater speed than previously possible. SPARC solves the compressible Navier-Stokes and Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equations for both laminar and turbulent flow. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Paul Crozier.
XyceRad
The XyceRad Parallel Electronic Simulator is a SPICE-compatible circuit simulator, that is designed to run on large-scale parallel computing platforms, though it also executes efficiently on a variety of architectures, including single processor workstations. As a mature platform for large-scale parallel circuit simulation, Xyce supports standard capabilities available from commercial simulators, in addition to a variety of devices and models specific to Sandia’s needs. For more information about Xyce please visit the Xyce website. If you are interested in obtaining this software please contact Shahed Reza.